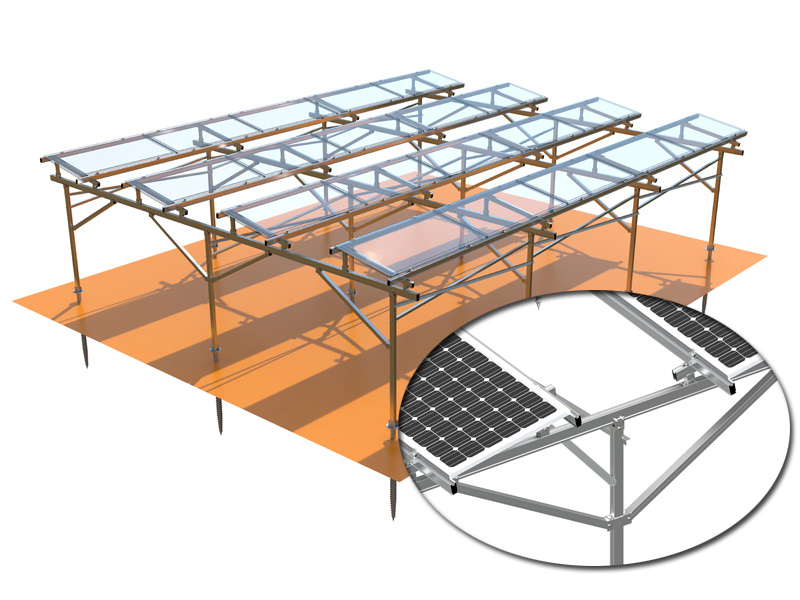
The versatility of the vertical bifacial solar panels system makes it suitable for various applications. In urban environments, these panels can be installed on the sides of buildings, transforming them into energy-generating structures. They can also be integrated into noise barriers along highways or railways, providing dual benefits of noise reduction and renewable energy generation. Additionally, this system can be deployed in agricultural settings, where vertical installations can coexist with crop cultivation, optimizing land use.
Item Name :
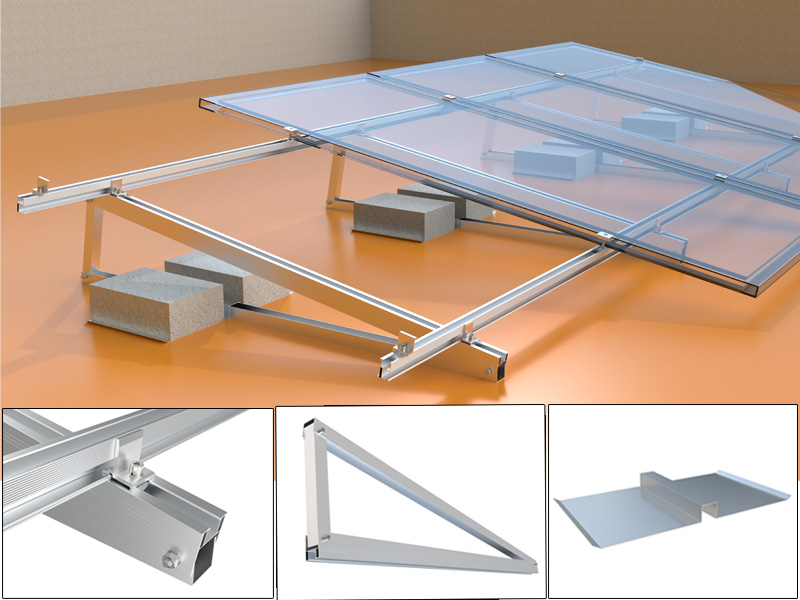
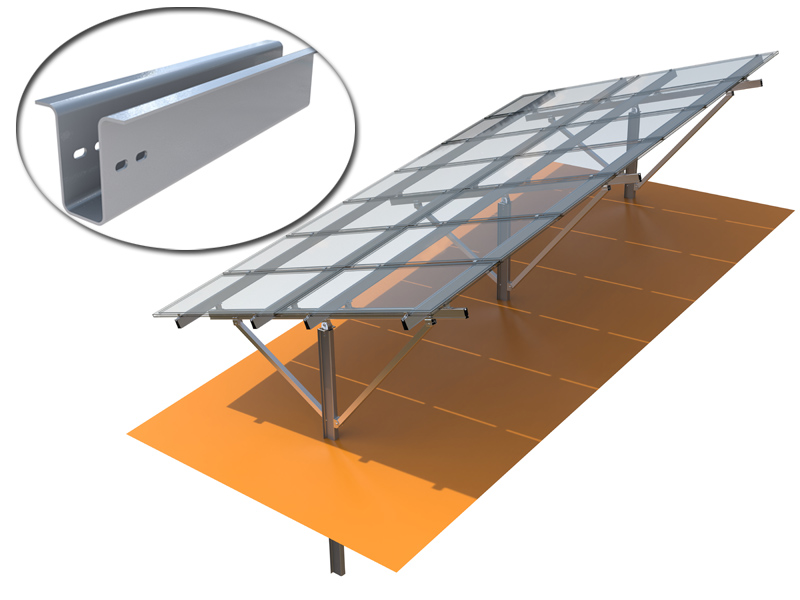
Vertical Bifacial Photovoltaic SystemsStandard :
S/NZS 1170, JISC8955-2017Application :
Open Space, FarmMaterial :
Aluminum/SteelWarranty :
12 yearsCustom :
Yes, customizedLead Time :
15-18 daysSample :
AvailablePhotovoltaic Systems with Vertically Mounted Bifacial PV Module
![]()
The agrivoltaic systems bifacial photovoltaics not only captures sunlight from both sides but also takes advantage of ground reflection. Sunlight that hits the ground is reflected back towards the panels, providing an additional source of solar energy. This reflected light is absorbed by the back surface of the panels, further increasing the overall power generation capacity. By harnessing both direct sunlight and ground-reflected light, this system maximizes energy production throughout the day.
Feature:
A. Increased Power Generation
B. Unique advantage in terms of space optimization
C. Increase in overall power output compared to conventional systems
D. Install on acoustic barriers on motorways, fences and urban facades
![]()


 About It
About It 

Vertically mounted agrivoltaic systems are innovative solar mounting solutions that combine solar energy generation with agricultural practices. In these systems, solar panels are installed vertically in agricultural fields, allowing for the simultaneous production of renewable energy and cultivation of crops. By utilizing vertical space, agrivoltaic systems optimize land use efficiency. Farmers can generate clean energy while still utilizing the land for agricultural purposes. This dual-use approach maximizes the productivity of the land and provides additional income streams for farmers.
![]()
![]()
